Nutrition in Animals
Nutrition in Animals: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Human Teeth, Nutrition in Amoebae, Digestion in Ruminants, Characteristics of Ruminants, Stomach of Ruminants, Molars, Nutrition in Animals, Digestion of Cellulose, Digestion, Assimilation of Food, Rumen, etc.
Important Questions on Nutrition in Animals
Sheep is ruminant animal.
All herbivores are ruminants.
Choose the ruminant animal.
Define the process of rumination.
The process of rumination is assisted by the presence of bacteria in the rumen.
_____ is the primary site of microbial digestion in ruminants.
Digestion in ruminants occurs sequentially in a four-chambered stomach.
The A, B and C are three living organisms. The organism A is a unicellular fungus which can live without air. It is used in the commercial production of an organic compound P from molasses. The organism B is a unicellular animal which lives in water and feeds and moves by using pseudopodia. It breathes through an organelle Q. The organism C is a tiny animal which acts as a carrier of the malarial parasite. It breathes and respires through a kind of tiny holes R and air-tubes S in its body.
What is organism B and organelle Q?
The excess glucose is stored in the liver as glycogen.
_____ is the hardest substance in our body.
The outer layer of a tooth is called

Tina is years old and her child, Emma is years old. Based on this, which of these statements is correct?
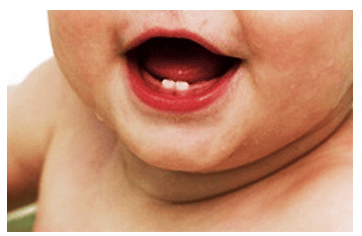
George is seven months old and he has newly developed teeth. What are these teeth known as?
State true or false.
A human being produces two sets of 32 teeth each during their lifetime.

Anna is six years old. She is excited because she has just lost her first tooth naturally. What kind of tooth has she lost?
Identify the set of permanent teeth.
Another name for milk teeth is temporary teeth. Why?
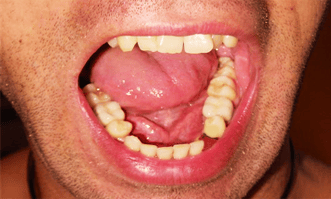
Every time we lose a tooth, it is replaced by a new one.
